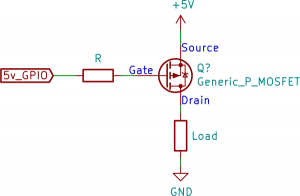
IDSS (referred to as the drain current for zero bias) is the maximum current that flowsthrough a FET transistor, which is when the gate voltage, VG, supplied to the FET is 0V.
1) Electronics: fet channel, field effect transistor channel 2) Makarov: channel of a field effect transistor. Clean memory for mac. ‘N-channel’ and ‘p-channel’ versions of both types of FET are available, just as normal transistors are available in npn and pnp versions. Figure 1 shows the symbols and supply polarities of both types of bipolar transistor, and compares them with both JFET versions.

Fet Diagram
When the gate voltage decreases for N-Channel FETs, or increases for P-Channel FETs, the drain current ID becomes smaller and smaller, until after a certain threshold, the transistor shuts off.
The current, IDSS, is important because it's the maximum current that a FET can reach without entering the restricted breakdown region. It is the maximum current in the tolerance range of drain-source voltages, VDS, that can be achieved.
IDSS is referred to as the drain current for zero bias, because the gate-source voltagerequires no bias voltage to operate. The gate-source voltage is just zero. No voltage needs to be applied to it.
N Type Fet
N Channel Fet Operation
